Java Adapter Classes
Java adapter classes provide the default implementation of listener interfaces. If you inherit the adapter class, you will not be forced to provide the implementation of all the methods of listener interfaces. So it saves code.
The adapter classes are found in java.awt.event, java.awt.dnd and javax.swing.event packages. The Adapter classes with their corresponding listener interfaces are given below.
java.awt.event Adapter classes
| Adapter class | Listener interface |
|---|---|
| WindowAdapter | WindowListener |
| KeyAdapter | KeyListener |
| MouseAdapter | MouseListener |
| MouseMotionAdapter | MouseMotionListener |
| FocusAdapter | FocusListener |
| ComponentAdapter | ComponentListener |
| ContainerAdapter | ContainerListener |
| HierarchyBoundsAdapter | HierarchyBoundsListener |
java.awt.dnd Adapter classes
| Adapter class | Listener interface |
|---|---|
| DragSourceAdapter | DragSourceListener |
| DragTargetAdapter | DragTargetListener |
javax.swing.event Adapter classes
| Adapter class | Listener interface |
|---|---|
| MouseInputAdapter | MouseInputListener |
| InternalFrameAdapter | InternalFrameListener |
Java WindowAdapter Example
Output:
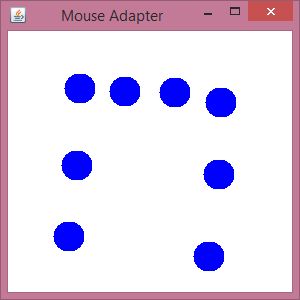
Java MouseAdapter Example
Output:
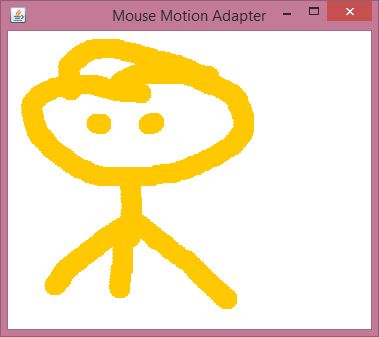
Java MouseMotionAdapter Example
Output:
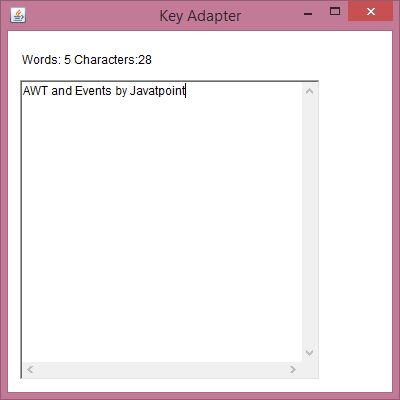
Java KeyAdapter Example
Output:
arvesorp-ma Heather Wang https://wakelet.com/wake/72F3YCmDHnaBQf7onGyau
ReplyDeletefromiztralvi
tracicWrio-do Carlos Ruiz program
ReplyDeleteSoftware
carnidoma