Java JButton
The JButton class is used to create a labeled button that has platform independent implementation. The application result in some action when the button is pushed. It inherits AbstractButton class.
JButton class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JButton class.
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JButton() | It creates a button with no text and icon. |
| JButton(String s) | It creates a button with the specified text. |
| JButton(Icon i) | It creates a button with the specified icon object. |
Commonly used Methods of AbstractButton class:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| void setText(String s) | It is used to set specified text on button |
| String getText() | It is used to return the text of the button. |
| void setEnabled(boolean b) | It is used to enable or disable the button. |
| void setIcon(Icon b) | It is used to set the specified Icon on the button. |
| Icon getIcon() | It is used to get the Icon of the button. |
| void setMnemonic(int a) | It is used to set the mnemonic on the button. |
| void addActionListener(ActionListener a) | It is used to add the action listener to this object. |
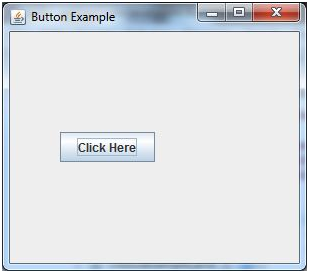
Java JButton Example
Output:
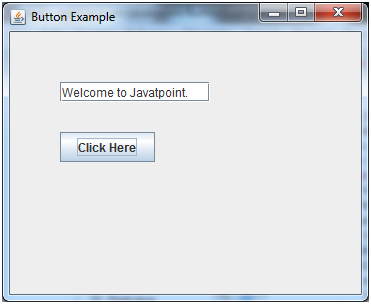
Java JButton Example with ActionListener
Output:
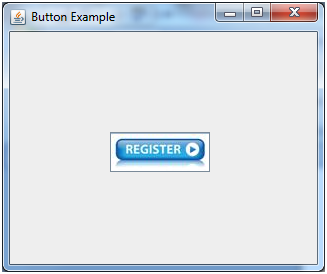
Example of displaying image on the button:
Output:
ava JLabel
The object of JLabel class is a component for placing text in a container. It is used to display a single line of read only text. The text can be changed by an application but a user cannot edit it directly. It inherits JComponent class.
JLabel class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JLabel class.
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JLabel() | Creates a JLabel instance with no image and with an empty string for the title. |
| JLabel(String s) | Creates a JLabel instance with the specified text. |
| JLabel(Icon i) | Creates a JLabel instance with the specified image. |
| JLabel(String s, Icon i, int horizontalAlignment) | Creates a JLabel instance with the specified text, image, and horizontal alignment. |
Commonly used Methods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| String getText() | t returns the text string that a label displays. |
| void setText(String text) | It defines the single line of text this component will display. |
| void setHorizontalAlignment(int alignment) | It sets the alignment of the label's contents along the X axis. |
| Icon getIcon() | It returns the graphic image that the label displays. |
| int getHorizontalAlignment() | It returns the alignment of the label's contents along the X axis. |
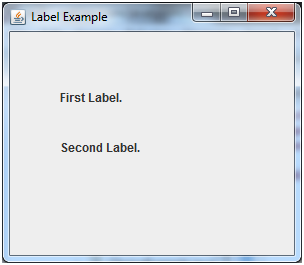
Java JLabel Example
Output:
Java JLabel Example with ActionListener
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment