Java AWT Panel
The Panel is a simplest container class. It provides space in which an application can attach any other component. It inherits the Container class.
It doesn't have title bar.
AWT Panel class declaration
- public class Panel extends Container implements Accessible
Java AWT Panel Example
- import java.awt.*;
- public class PanelExample {
- PanelExample()
- {
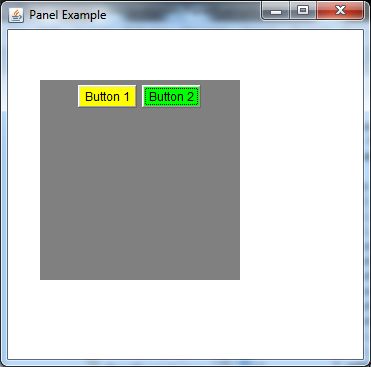
- Frame f= new Frame("Panel Example");
- Panel panel=new Panel();
- panel.setBounds(40,80,200,200);
- panel.setBackground(Color.gray);
- Button b1=new Button("Button 1");
- b1.setBounds(50,100,80,30);
- b1.setBackground(Color.yellow);
- Button b2=new Button("Button 2");
- b2.setBounds(100,100,80,30);
- b2.setBackground(Color.green);
- panel.add(b1); panel.add(b2);
- f.add(panel);
- f.setSize(400,400);
- f.setLayout(null);
- f.setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String args[])
- {
- new PanelExample();
- }
- }
Output:
Java AWT Dialog
The Dialog control represents a top level window with a border and a title used to take some form of input from the user. It inherits the Window class.
Unlike Frame, it doesn't have maximize and minimize buttons.
Frame vs Dialog
Frame and Dialog both inherits Window class. Frame has maximize and minimize buttons but Dialog doesn't have.
AWT Dialog class declaration
- public class Dialog extends Window
Java AWT Dialog Example
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- public class DialogExample {
- private static Dialog d;
- DialogExample() {
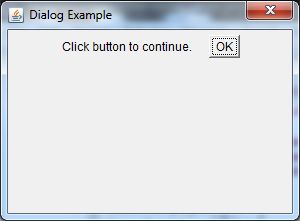
- Frame f= new Frame();
- d = new Dialog(f , "Dialog Example", true);
- d.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
- Button b = new Button ("OK");
- b.addActionListener ( new ActionListener()
- {
- public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent e )
- {
- DialogExample.d.setVisible(false);
- }
- });
- d.add( new Label ("Click button to continue."));
- d.add(b);
- d.setSize(300,300);
- d.setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String args[])
- {
- new DialogExample();
- }
- }
Output:
Java AWT Toolkit
Toolkit class is the abstract superclass of every implementation in the Abstract Window Toolkit. Subclasses of Toolkit are used to bind various components. It inherits Object class.
AWT Toolkit class declaration
- public abstract class Toolkit extends Object
Java AWT Toolkit Example
- import java.awt.*;
- public class ToolkitExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Toolkit t = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
- System.out.println("Screen resolution = " + t.getScreenResolution());
- Dimension d = t.getScreenSize();
- System.out.println("Screen width = " + d.width);
- System.out.println("Screen height = " + d.height);
- }
- }
Output:
Screen resolution = 96
Screen width = 1366
Screen height = 768
Java AWT Toolkit Example: beep()
- import java.awt.event.*;
- public class ToolkitExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
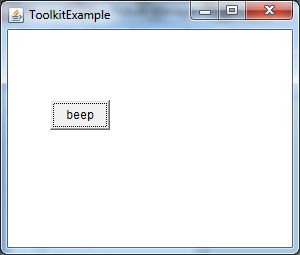
- Frame f=new Frame("ToolkitExample");
- Button b=new Button("beep");
- b.setBounds(50,100,60,30);
- f.add(b);
- f.setSize(300,300);
- f.setLayout(null);
- f.setVisible(true);
- b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
- Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
- }
- });
- }
- }
Output:
Java AWT Toolkit Example: Change TitleBar Icon
- import java.awt.*;
- class ToolkitExample {
- ToolkitExample(){
- Frame f=new Frame();
- Image icon = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getImage("D:\\icon.png");
- f.setIconImage(icon);
- f.setLayout(null);
- f.setSize(400,400);
- f.setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- new ToolkitExample();
- }
- }
Output:
Anurag Rana
Educator CSE/IT




Comments
Post a Comment