Java JSeparator
The object of JSeparator class is used to provide a general purpose component for implementing divider lines. It is used to draw a line to separate widgets in a Layout. It inherits JComponent class.
JSeparator class declaration
Commonly used Constructors of JSeparator
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JSeparator() | Creates a new horizontal separator. |
| JSeparator(int orientation) | Creates a new separator with the specified horizontal or vertical orientation. |
Commonly used Methods of JSeparator
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void setOrientation(int orientation) | It is used to set the orientation of the separator. |
| int getOrientation() | It is used to return the orientation of the separator. |
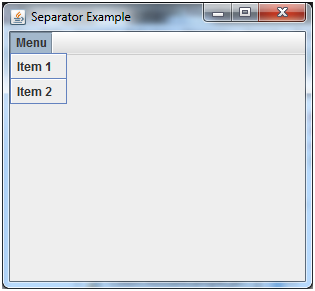
Java JSeparator Example 1
Output:
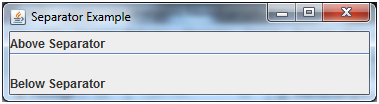
Java JSeparator Example 2
Output:
Java JProgressBar
The JProgressBar class is used to display the progress of the task. It inherits JComponent class.
JProgressBar class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JProgressBar class.
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JProgressBar() | It is used to create a horizontal progress bar but no string text. |
| JProgressBar(int min, int max) | It is used to create a horizontal progress bar with the specified minimum and maximum value. |
| JProgressBar(int orient) | It is used to create a progress bar with the specified orientation, it can be either Vertical or Horizontal by using SwingConstants.VERTICAL and SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL constants. |
| JProgressBar(int orient, int min, int max) | It is used to create a progress bar with the specified orientation, minimum and maximum value. |
Commonly used Methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void setStringPainted(boolean b) | It is used to determine whether string should be displayed. |
| void setString(String s) | It is used to set value to the progress string. |
| void setOrientation(int orientation) | It is used to set the orientation, it may be either vertical or horizontal by using SwingConstants.VERTICAL and SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL constants. |
| void setValue(int value) | It is used to set the current value on the progress bar. |
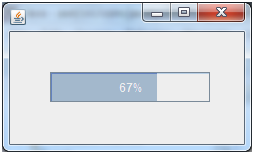
Java JProgressBar Example
Output:
Java JTree
The JTree class is used to display the tree structured data or hierarchical data. JTree is a complex component. It has a 'root node' at the top most which is a parent for all nodes in the tree. It inherits JComponent class.
JTree class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JTree class.
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JTree() | Creates a JTree with a sample model. |
| JTree(Object[] value) | Creates a JTree with every element of the specified array as the child of a new root node. |
| JTree(TreeNode root) | Creates a JTree with the specified TreeNode as its root, which displays the root node. |
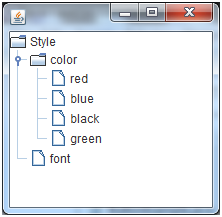
Java JTree Example
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment