Java JToolBar
JToolBar container allows us to group other components, usually buttons with icons in a row or column. JToolBar provides a component which is useful for displaying commonly used actions or controls.
Nested Classes
| Modifier and Type | Class | Description |
|---|
| protected class | JToolBar.AccessibleJToolBar | This class implements accessibility support for the JToolBar class. |
| static class | JToolBar.Separator | A toolbar-specific separator. |
Constructors
| Constructor | Description |
|---|
| JToolBar() | It creates a new tool bar; orientation defaults to HORIZONTAL. |
| JToolBar(int orientation) | It creates a new tool bar with the specified orientation. |
| JToolBar(String name) | It creates a new tool bar with the specified name. |
| JToolBar(String name, int orientation) | It creates a new tool bar with a specified name and orientation. |
Useful Methods
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|
| JButton | add(Action a) | It adds a new JButton which dispatches the action. |
| protected void | addImpl(Component comp, Object constraints, int index) | If a JButton is being added, it is initially set to be disabled. |
| void | addSeparator() | It appends a separator of default size to the end of the tool bar. |
| protected PropertyChangeListener | createActionChangeListener(JButton b) | It returns a properly configured PropertyChangeListener which updates the control as changes to the Action occur, or null if the default property change listener for the control is desired. |
| protected JButton | createActionComponent(Action a) | Factory method which creates the JButton for Actions added to the JToolBar. |
| ToolBarUI | getUI() | It returns the tool bar's current UI. |
| void | setUI(ToolBarUI ui) | It sets the L&F object that renders this component. |
| void | setOrientation(int o) | It sets the orientation of the tool bar. |
Java JToolBar Example
- import java.awt.BorderLayout;
- import java.awt.Container;
- import javax.swing.JButton;
- import javax.swing.JComboBox;
- import javax.swing.JFrame;
- import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
- import javax.swing.JTextArea;
- import javax.swing.JToolBar;
-
- public class JToolBarExample {
- public static void main(final String args[]) {
- JFrame myframe = new JFrame("JToolBar Example");
- myframe.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
- JToolBar toolbar = new JToolBar();
- toolbar.setRollover(true);
- JButton button = new JButton("File");
- toolbar.add(button);
- toolbar.addSeparator();
- toolbar.add(new JButton("Edit"));
- toolbar.add(new JComboBox(new String[] { "Opt-1", "Opt-2", "Opt-3", "Opt-4" }));
- Container contentPane = myframe.getContentPane();
- contentPane.add(toolbar, BorderLayout.NORTH);
- JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea();
- JScrollPane mypane = new JScrollPane(textArea);
- contentPane.add(mypane, BorderLayout.EAST);
- myframe.setSize(450, 250);
- myframe.setVisible(true);
- }
- }
Java JViewport
The JViewport class is used to implement scrolling. JViewport is designed to support both logical scrolling and pixel-based scrolling. The viewport's child, called the view, is scrolled by calling the JViewport.setViewPosition() method.
Nested Classes
| Modifier and Type | Class | Description |
|---|
| protected class | JViewport.AccessibleJViewport | This class implements accessibility support for the Jviewport class. |
| protected class | JViewport.ViewListener | A listener for the view. |
Fields
| Modifier and Type | Field | Description |
|---|
| static int | BACKINGSTORE_SCROLL_MODE | It draws viewport contents into an offscreen image. |
| protected Image | backingStoreImage | The view image used for a backing store. |
| static int | BLIT_SCROLL_MODE | It uses graphics.copyArea to implement scrolling. |
| protected boolean | isViewSizeSet | True when the viewport dimensions have been determined. |
| protected Point | lastPaintPosition | The last viewPosition that we've painted, so we know how much of the backing store image is valid. |
| protected boolean | scrollUnderway | The scrollUnderway flag is used for components like JList. |
| static int | SIMPLE_SCROLL_MODE | This mode uses the very simple method of redrawing the entire contents of the scrollpane each time it is scrolled. |
Constructor
| Constructor | Description |
|---|
| JViewport() | Creates a JViewport. |
Methods
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|
| void | addChangeListener(ChangeListener l) | It adds a ChangeListener to the list that is notified each time the view's size, position, or the viewport's extent size has changed. |
| protected LayoutManager | createLayoutManager() | Subclassers can override this to install a different layout manager (or null) in the constructor. |
| protected Jviewport.ViewListener | createViewListener() | It creates a listener for the view. |
| int | getScrollMode() | It returns the current scrolling mode. |
| Component | getView() | It returns the JViewport's one child or null. |
| Point | getViewPosition() | It returns the view coordinates that appear in the upper left hand corner of the viewport, or 0,0 if there's no view. |
| Dimension | getViewSize() | If the view's size hasn't been explicitly set, return the preferred size, otherwise return the view's current size. |
| void | setExtentSize(Dimension newExtent) | It sets the size of the visible part of the view using view coordinates. |
| void | setScrollMode(int mode) | It used to control the method of scrolling the viewport contents. |
| void | setViewSize(Dimension newSize) | It sets the size of the view. |
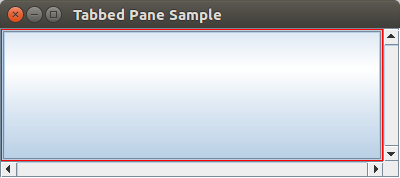
JViewport Example
- import java.awt.BorderLayout;
- import java.awt.Color;
- import java.awt.Dimension;
- import javax.swing.JButton;
- import javax.swing.JFrame;
- import javax.swing.JLabel;
- import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
- import javax.swing.border.LineBorder;
- public class ViewPortClass2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- JFrame frame = new JFrame("Tabbed Pane Sample");
- frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
-
- JLabel label = new JLabel("Label");
- label.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(1000, 1000));
- JScrollPane jScrollPane = new JScrollPane(label);
-
- JButton jButton1 = new JButton();
- jScrollPane.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(JScrollPane.HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS);
- jScrollPane.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(JScrollPane.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS);
- jScrollPane.setViewportBorder(new LineBorder(Color.RED));
- jScrollPane.getViewport().add(jButton1, null);
-
- frame.add(jScrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
- frame.setSize(400, 150);
- frame.setVisible(true);
- }
- }
Output:
Java JFrame
The javax.swing.JFrame class is a type of container which inherits the java.awt.Frame class. JFrame works like the main window where components like labels, buttons, textfields are added to create a GUI.
Unlike Frame, JFrame has the option to hide or close the window with the help of setDefaultCloseOperation(int) method.
Nested Class
| Modifier and Type | Class | Description |
|---|
| protected class | JFrame.AccessibleJFrame | This class implements accessibility support for the JFrame class. |
Fields
| Modifier and Type | Field | Description |
|---|
| protected AccessibleContext | accessibleContext | The accessible context property. |
| static int | EXIT_ON_CLOSE | The exit application default window close operation. |
| protected JRootPane | rootPane | The JRootPane instance that manages the contentPane and optional menuBar for this frame, as well as the glassPane. |
| protected boolean | rootPaneCheckingEnabled | If true then calls to add and setLayout will be forwarded to the contentPane. |
Constructors
| Constructor | Description |
|---|
| JFrame() | It constructs a new frame that is initially invisible. |
| JFrame(GraphicsConfiguration gc) | It creates a Frame in the specified GraphicsConfiguration of a screen device and a blank title. |
| JFrame(String title) | It creates a new, initially invisible Frame with the specified title. |
| JFrame(String title, GraphicsConfiguration gc) | It creates a JFrame with the specified title and the specified GraphicsConfiguration of a screen device. |
Useful Methods
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|
| protected void | addImpl(Component comp, Object constraints, int index) | Adds the specified child Component. |
| protected JRootPane | createRootPane() | Called by the constructor methods to create the default rootPane. |
| protected void | frameInit() | Called by the constructors to init the JFrame properly. |
| void | setContentPane(Containe contentPane) | It sets the contentPane property |
| static void | setDefaultLookAndFeelDecorated(boolean defaultLookAndFeelDecorated) | Provides a hint as to whether or not newly created JFrames should have their Window decorations (such as borders, widgets to close the window, title...) provided by the current look and feel. |
| void | setIconImage(Image image) | It sets the image to be displayed as the icon for this window. |
| void | setJMenuBar(JMenuBar menubar) | It sets the menubar for this frame. |
| void | setLayeredPane(JLayeredPane layeredPane) | It sets the layeredPane property. |
| JRootPane | getRootPane() | It returns the rootPane object for this frame. |
| TransferHandler | getTransferHandler() | It gets the transferHandler property. |
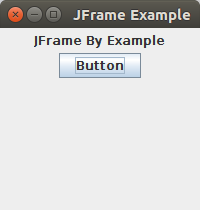
JFrame Example
- import java.awt.FlowLayout;
- import javax.swing.JButton;
- import javax.swing.JFrame;
- import javax.swing.JLabel;
- import javax.swing.Jpanel;
- public class JFrameExample {
- public static void main(String s[]) {
- JFrame frame = new JFrame("JFrame Example");
- JPanel panel = new JPanel();
- panel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
- JLabel label = new JLabel("JFrame By Example");
- JButton button = new JButton();
- button.setText("Button");
- panel.add(label);
- panel.add(button);
- frame.add(panel);
- frame.setSize(200, 300);
- frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
- frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
- frame.setVisible(true);
- }
- }
Output
Anurag Rana
Educator CSE/IT


Comments
Post a Comment