Java Networking
Java Networking is a concept of connecting two or more computing devices together so that we can share resources.
Java socket programming provides facility to share data between different computing devices.
Advantage of Java Networking
- sharing resources
- centralize software management
Java Networking Terminology
The widely used java networking terminologies are given below:
- IP Address
- Protocol
- Port Number
- MAC Address
- Connection-oriented and connection-less protocol
- Socket
1) IP Address
IP address is a unique number assigned to a node of a network e.g. 192.168.0.1 . It is composed of octets that range from 0 to 255.
It is a logical address that can be changed.
2) Protocol
A protocol is a set of rules basically that is followed for communication. For example:
- TCP
- FTP
- Telnet
- SMTP
- POP etc.
3) Port Number
The port number is used to uniquely identify different applications. It acts as a communication endpoint between applications.
The port number is associated with the IP address for communication between two applications.
4) MAC Address
MAC (Media Access Control) Address is a unique identifier of NIC (Network Interface Controller). A network node can have multiple NIC but each with unique MAC.
5) Connection-oriented and connection-less protocol
In connection-oriented protocol, acknowledgement is sent by the receiver. So it is reliable but slow. The example of connection-oriented protocol is TCP.
But, in connection-less protocol, acknowledgement is not sent by the receiver. So it is not reliable but fast. The example of connection-less protocol is UDP.
6) Socket
A socket is an endpoint between two way communication.
Visit next page for java socket programming.
java.net package
The java.net package provides many classes to deal with networking applications in Java. A list of these classes is given below:
- Authenticator
- CacheRequest
- CacheResponse
- ContentHandler
- CookieHandler
- CookieManager
- DatagramPacket
- DatagramSocket
- DatagramSocketImpl
- InterfaceAddress
- JarURLConnection
- MulticastSocket
- InetSocketAddress
- InetAddress
- Inet4Address
- Inet6Address
- IDN
- HttpURLConnection
- HttpCookie
- NetPermission
- NetworkInterface
- PasswordAuthentication
- Proxy
- ProxySelector
- ResponseCache
- SecureCacheResponse
- ServerSocket
- Socket
- SocketAddress
- SocketImpl
- SocketPermission
- StandardSocketOptions
- URI
- URL
- URLClassLoader
- URLConnection
- URLDecoder
- URLEncoder
- URLStreamHandler
Java Socket Programming
Java Socket programming is used for communication between the applications running on different JRE.
Java Socket programming can be connection-oriented or connection-less.
Socket and ServerSocket classes are used for connection-oriented socket programming and DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket classes are used for connection-less socket programming.
The client in socket programming must know two information:
- IP Address of Server, and
- Port number.
Here, we are going to make one-way client and server communication. In this application, client sends a message to the server, server reads the message and prints it. Here, two classes are being used: Socket and ServerSocket. The Socket class is used to communicate client and server. Through this class, we can read and write message. The ServerSocket class is used at server-side. The accept() method of ServerSocket class blocks the console until the client is connected. After the successful connection of client, it returns the instance of Socket at server-side.
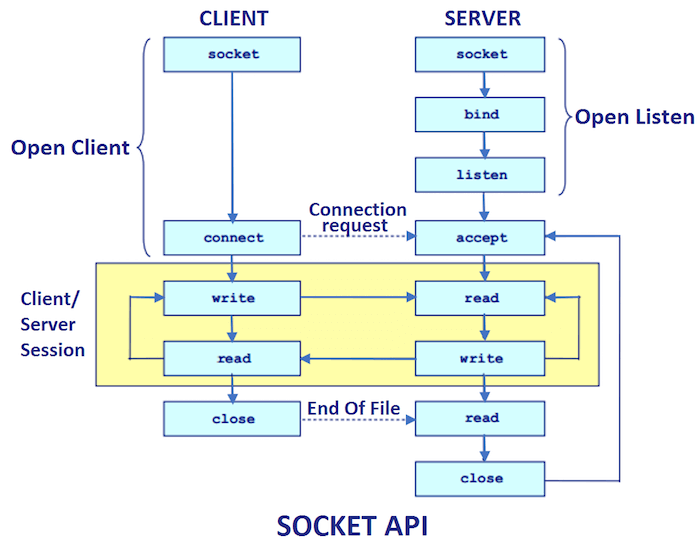
Socket class
A socket is simply an endpoint for communications between the machines. The Socket class can be used to create a socket.
Important methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1) public InputStream getInputStream() | returns the InputStream attached with this socket. |
| 2) public OutputStream getOutputStream() | returns the OutputStream attached with this socket. |
| 3) public synchronized void close() | closes this socket |
ServerSocket class
The ServerSocket class can be used to create a server socket. This object is used to establish communication with the clients.
Important methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1) public Socket accept() | returns the socket and establish a connection between server and client. |
| 2) public synchronized void close() | closes the server socket. |
Example of Java Socket Programming
Creating Server:
To create the server application, we need to create the instance of ServerSocket class. Here, we are using 6666 port number for the communication between the client and server. You may also choose any other port number. The accept() method waits for the client. If clients connects with the given port number, it returns an instance of Socket.
Creating Client:
To create the client application, we need to create the instance of Socket class. Here, we need to pass the IP address or hostname of the Server and a port number. Here, we are using "localhost" because our server is running on same system.
Let's see a simple of Java socket programming where client sends a text and server receives and prints it.
File: MyServer.java
File: MyClient.java
Example of Java Socket Programming (Read-Write both side)
In this example, client will write first to the server then server will receive and print the text. Then server will write to the client and client will receive and print the text. The step goes on.
File: MyServer.java
File: MyClient.java
Comments
Post a Comment