Steps to perform Event Handling
Following steps are required to perform event handling:
- Register the component with the Listener
Registration Methods
For registering the component with the Listener, many classes provide the registration methods. For example:
- Button
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- MenuItem
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- TextField
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- public void addTextListener(TextListener a){}
- TextArea
- public void addTextListener(TextListener a){}
- Checkbox
- public void addItemListener(ItemListener a){}
- Choice
- public void addItemListener(ItemListener a){}
- List
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- public void addItemListener(ItemListener a){}
Java Event Handling Code
We can put the event handling code into one of the following places:
- Within class
- Other class
- Anonymous class
Java event handling by implementing ActionListener
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
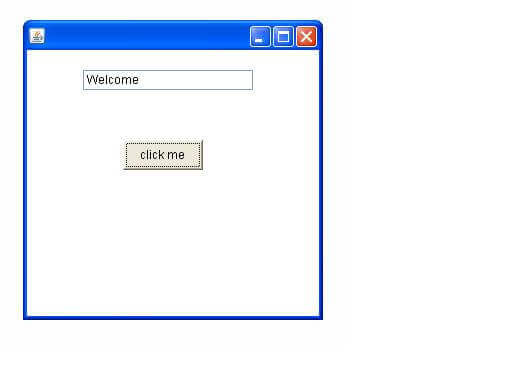
- class AEvent extends Frame implements ActionListener{
- TextField tf;
- AEvent(){
-
-
- tf=new TextField();
- tf.setBounds(60,50,170,20);
- Button b=new Button("click me");
- b.setBounds(100,120,80,30);
-
-
- b.addActionListener(this);
-
-
- add(b);add(tf);
- setSize(300,300);
- setLayout(null);
- setVisible(true);
- }
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
- tf.setText("Welcome");
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- new AEvent();
- }
- }
public void setBounds(int xaxis, int yaxis, int width, int height); have been used in the above example that sets the position of the component it may be button, textfield etc.
2) Java event handling by outer class
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- class AEvent2 extends Frame{
- TextField tf;
- AEvent2(){
-
- tf=new TextField();
- tf.setBounds(60,50,170,20);
- Button b=new Button("click me");
- b.setBounds(100,120,80,30);
-
- Outer o=new Outer(this);
- b.addActionListener(o);
-
- add(b);add(tf);
- setSize(300,300);
- setLayout(null);
- setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- new AEvent2();
- }
- }
- import java.awt.event.*;
- class Outer implements ActionListener{
- AEvent2 obj;
- Outer(AEvent2 obj){
- this.obj=obj;
- }
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
- obj.tf.setText("welcome");
- }
- }
3) Java event handling by anonymous class
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- class AEvent3 extends Frame{
- TextField tf;
- AEvent3(){
- tf=new TextField();
- tf.setBounds(60,50,170,20);
- Button b=new Button("click me");
- b.setBounds(50,120,80,30);
-
- b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
- public void actionPerformed(){
- tf.setText("hello");
- }
- });
- add(b);add(tf);
- setSize(300,300);
- setLayout(null);
- setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- new AEvent3();
- }
- }

Comments
Post a Comment