Java AWT Tutorial
Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) is an API to develop GUI or window-based applications in java.
Java AWT components are platform-dependent i.e. components are displayed according to the view of operating system. AWT is heavyweight i.e. its components are using the resources of OS.
The java.awt package provides classes for AWT api such as TextField, Label, TextArea, RadioButton, CheckBox, Choice, List etc.
Java AWT Hierarchy
The hierarchy of Java AWT classes are given below.
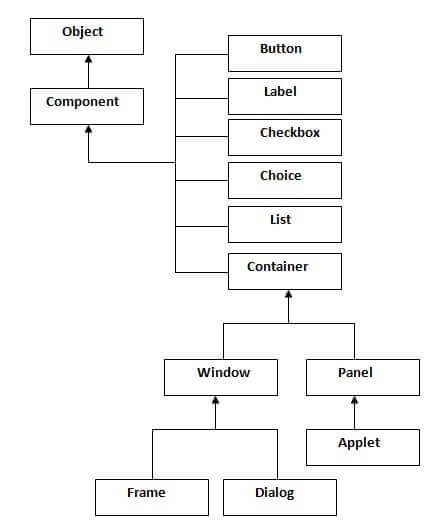
Container
The Container is a component in AWT that can contain another components like buttons, textfields, labels etc. The classes that extends Container class are known as container such as Frame, Dialog and Panel.
Window
The window is the container that have no borders and menu bars. You must use frame, dialog or another window for creating a window.
Panel
The Panel is the container that doesn't contain title bar and menu bars. It can have other components like button, textfield etc.
Frame
The Frame is the container that contain title bar and can have menu bars. It can have other components like button, textfield etc.
Useful Methods of Component class
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| public void add(Component c) | inserts a component on this component. |
| public void setSize(int width,int height) | sets the size (width and height) of the component. |
| public void setLayout(LayoutManager m) | defines the layout manager for the component. |
| public void setVisible(boolean status) | changes the visibility of the component, by default false. |
Java AWT Example
To create simple awt example, you need a frame. There are two ways to create a frame in AWT.
- By extending Frame class (inheritance)
- By creating the object of Frame class (association)
AWT Example by Inheritance
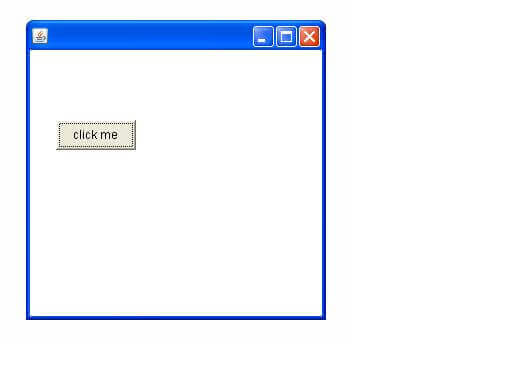
Let's see a simple example of AWT where we are inheriting Frame class. Here, we are showing Button component on the Frame.
The setBounds(int xaxis, int yaxis, int width, int height) method is used in the above example that sets the position of the awt button.
AWT Example by Association
Let's see a simple example of AWT where we are creating instance of Frame class. Here, we are showing Button component on the Frame.

Comments
Post a Comment