Java AWT Choice
The object of Choice class is used to show popup menu of choices. Choice selected by user is shown on the top of a menu. It inherits Component class.
AWT Choice Class Declaration
Java AWT Choice Example
Output:
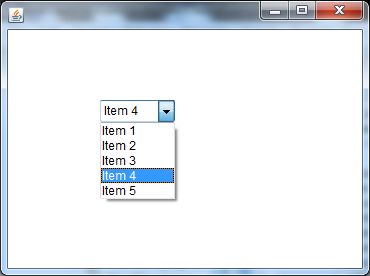
Java AWT Choice Example with ActionListener
Java AWT List
The object of List class represents a list of text items. By the help of list, user can choose either one item or multiple items. It inherits Component class.
AWT List class Declaration
Java AWT List Example
Output:
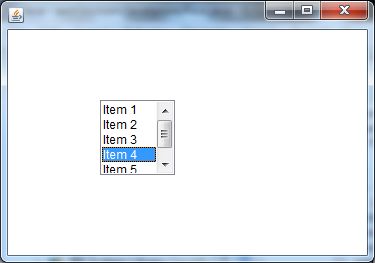
Java AWT List Example with ActionListener
Output:
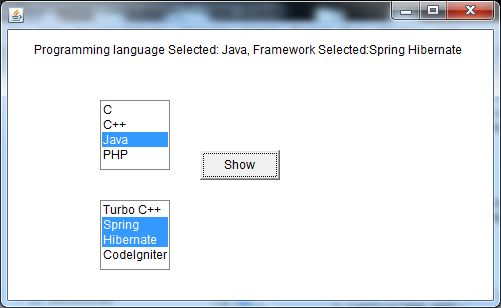
Java AWT Canvas
The Canvas control represents a blank rectangular area where the application can draw or trap input events from the user. It inherits the Component class.
Comments
Post a Comment