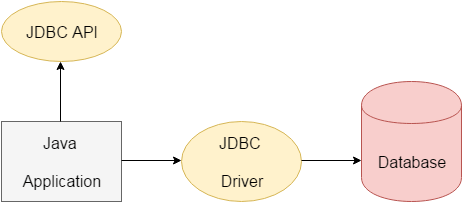
Java JDBC
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a Java API to connect and execute the query with the database. It is a part of JavaSE (Java Standard Edition). JDBC API uses JDBC drivers to connect with the database. There are four types of JDBC drivers:
- JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver,
- Native Driver,
- Network Protocol Driver, and
- Thin Driver
We have discussed the above four drivers in the next chapter.
We can use JDBC API to access tabular data stored in any relational database. By the help of JDBC API, we can save, update, delete and fetch data from the database. It is like Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) provided by Microsoft.
The current version of JDBC is 4.3. It is the stable release since 21st September, 2017. It is based on the X/Open SQL Call Level Interface. The java.sql package contains classes and interfaces for JDBC API. A list of popular interfaces of JDBC API are given below:
- Driver interface
- Connection interface
- Statement interface
- PreparedStatement interface
- CallableStatement interface
- ResultSet interface
- ResultSetMetaData interface
- DatabaseMetaData interface
- RowSet interface
A list of popular classes of JDBC API are given below:
- DriverManager class
- Blob class
- Clob class
- Types class
Why Should We Use JDBC
Before JDBC, ODBC API was the database API to connect and execute the query with the database. But, ODBC API uses ODBC driver which is written in C language (i.e. platform dependent and unsecured). That is why Java has defined its own API (JDBC API) that uses JDBC drivers (written in Java language).
We can use JDBC API to handle database using Java program and can perform the following activities:
- Connect to the database
- Execute queries and update statements to the database
- Retrieve the result received from the database.
JDBC Driver
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
|
1) JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
| The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver uses ODBC driver to connect to the database. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now discouraged because of thin driver. |
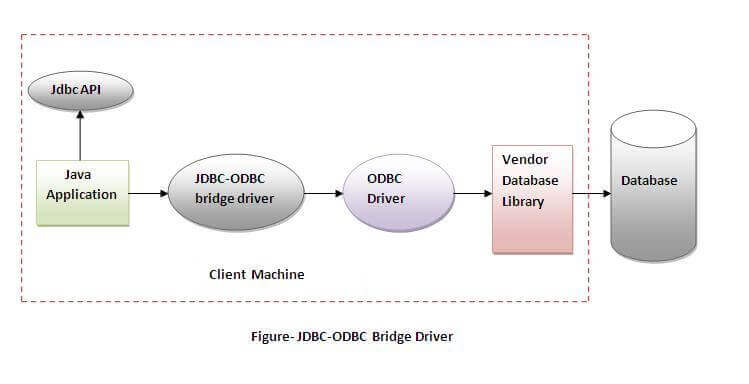
Oracle does not support the JDBC-ODBC Bridge from Java 8. Oracle recommends that you use JDBC drivers provided by the vendor of your database instead of the JDBC-ODBC Bridge.
Advantages:
- easy to use.
- can be easily connected to any database.
Disadvantages:
- Performance degraded because JDBC method call is converted into the ODBC function calls.
- The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client machine.
2) Native-API driver
| The Native API driver uses the client-side libraries of the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API. It is not written entirely in java. |
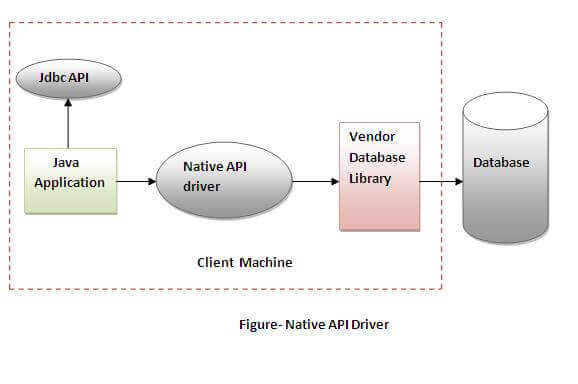
Advantage:
- performance upgraded than JDBC-ODBC bridge driver.
Disadvantage:
- The Native driver needs to be installed on the each client machine.
- The Vendor client library needs to be installed on client machine.
3) Network Protocol driver
The Network Protocol driver uses middleware (application server) that converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into the vendor-specific database protocol. It is fully written in java.
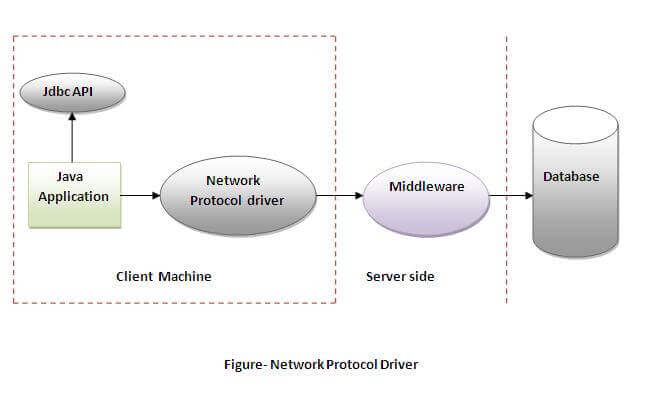
Advantage:
- No client side library is required because of application server that can perform many tasks like auditing, load balancing, logging etc.
Disadvantages:
- Network support is required on client machine.
- Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
- Maintenance of Network Protocol driver becomes costly because it requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
4) Thin driver
| The thin driver converts JDBC calls directly into the vendor-specific database protocol. That is why it is known as thin driver. It is fully written in Java language. |
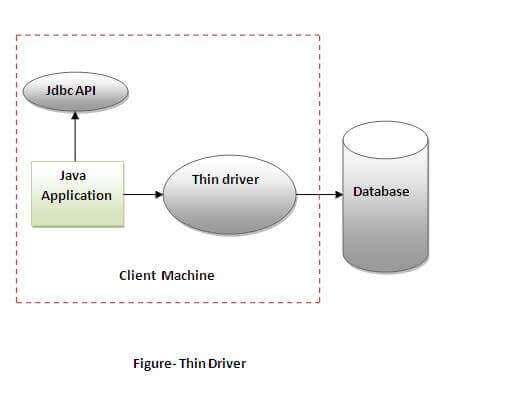
Advantage:
- Better performance than all other drivers.
- No software is required at client side or server side.
Disadvantage:
- Drivers depend on the Database.
Comments
Post a Comment