Java JTextField
The object of a JTextField class is a text component that allows the editing of a single line text. It inherits JTextComponent class.
JTextField class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JTextField class.
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JTextField() | Creates a new TextField |
| JTextField(String text) | Creates a new TextField initialized with the specified text. |
| JTextField(String text, int columns) | Creates a new TextField initialized with the specified text and columns. |
| JTextField(int columns) | Creates a new empty TextField with the specified number of columns. |
Commonly used Methods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| void addActionListener(ActionListener l) | It is used to add the specified action listener to receive action events from this textfield. |
| Action getAction() | It returns the currently set Action for this ActionEvent source, or null if no Action is set. |
| void setFont(Font f) | It is used to set the current font. |
| void removeActionListener(ActionListener l) | It is used to remove the specified action listener so that it no longer receives action events from this textfield. |
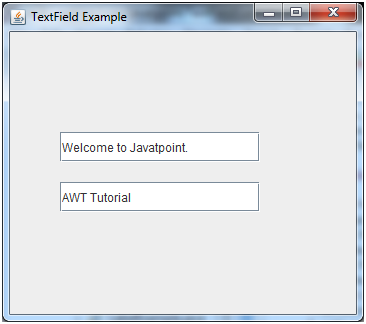
Java JTextField Example
Output:
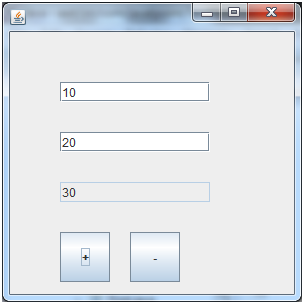
Java JTextField Example with ActionListener
Output:
Java JTextArea
The object of a JTextArea class is a multi line region that displays text. It allows the editing of multiple line text. It inherits JTextComponent class
JTextArea class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JTextArea class.
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| JTextArea() | Creates a text area that displays no text initially. |
| JTextArea(String s) | Creates a text area that displays specified text initially. |
| JTextArea(int row, int column) | Creates a text area with the specified number of rows and columns that displays no text initially. |
| JTextArea(String s, int row, int column) | Creates a text area with the specified number of rows and columns that displays specified text. |
Commonly used Methods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| void setRows(int rows) | It is used to set specified number of rows. |
| void setColumns(int cols) | It is used to set specified number of columns. |
| void setFont(Font f) | It is used to set the specified font. |
| void insert(String s, int position) | It is used to insert the specified text on the specified position. |
| void append(String s) | It is used to append the given text to the end of the document. |
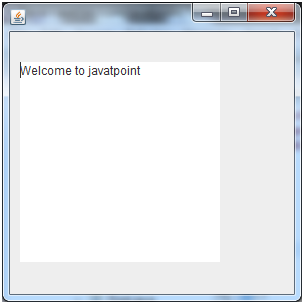
Java JTextArea Example
Output:
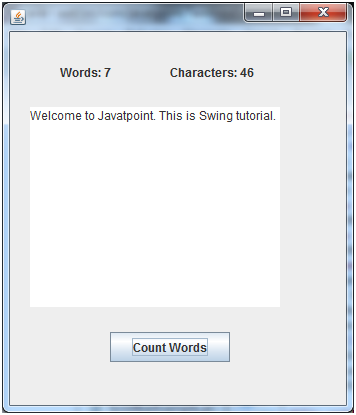
Java JTextArea Example with ActionListener
Output:
Comments
Post a Comment