Java ItemListener Interface
The Java ItemListener is notified whenever you click on the checkbox. It is notified against ItemEvent. The ItemListener interface is found in java.awt.event package. It has only one method: itemStateChanged().
itemStateChanged() method
The itemStateChanged() method is invoked automatically whenever you click or unclick on the registered checkbox component.
- public abstract void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e);
Java ItemListener Example
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- public class ItemListenerExample implements ItemListener{
- Checkbox checkBox1,checkBox2;
- Label label;
- ItemListenerExample(){
- Frame f= new Frame("CheckBox Example");
- label = new Label();
- label.setAlignment(Label.CENTER);
- label.setSize(400,100);
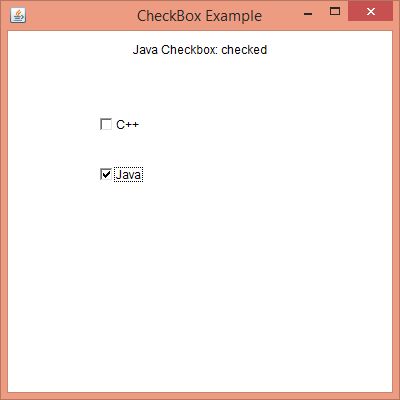
- checkBox1 = new Checkbox("C++");
- checkBox1.setBounds(100,100, 50,50);
- checkBox2 = new Checkbox("Java");
- checkBox2.setBounds(100,150, 50,50);
- f.add(checkBox1); f.add(checkBox2); f.add(label);
- checkBox1.addItemListener(this);
- checkBox2.addItemListener(this);
- f.setSize(400,400);
- f.setLayout(null);
- f.setVisible(true);
- }
- public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e) {
- if(e.getSource()==checkBox1)
- label.setText("C++ Checkbox: "
- + (e.getStateChange()==1?"checked":"unchecked"));
- if(e.getSource()==checkBox2)
- label.setText("Java Checkbox: "
- + (e.getStateChange()==1?"checked":"unchecked"));
- }
- public static void main(String args[])
- {
- new ItemListenerExample();
- }
- }
Output:
Java KeyListener Interface
The Java KeyListener is notified whenever you change the state of key. It is notified against KeyEvent. The KeyListener interface is found in java.awt.event package. It has three methods.
Methods of KeyListener interface
The signature of 3 methods found in KeyListener interface are given below:
- public abstract void keyPressed(KeyEvent e);
- public abstract void keyReleased(KeyEvent e);
- public abstract void keyTyped(KeyEvent e);
Java KeyListener Example
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- public class KeyListenerExample extends Frame implements KeyListener{
- Label l;
- TextArea area;
- KeyListenerExample(){
-
- l=new Label();
- l.setBounds(20,50,100,20);
- area=new TextArea();
- area.setBounds(20,80,300, 300);
- area.addKeyListener(this);
-
- add(l);add(area);
- setSize(400,400);
- setLayout(null);
- setVisible(true);
- }
- public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
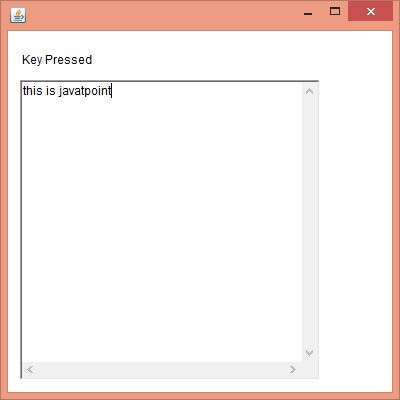
- l.setText("Key Pressed");
- }
- public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
- l.setText("Key Released");
- }
- public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {
- l.setText("Key Typed");
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- new KeyListenerExample();
- }
- }
Output:
Java WindowListener Interface
The Java WindowListener is notified whenever you change the state of window. It is notified against WindowEvent. The WindowListener interface is found in java.awt.event package. It has three methods.
Methods of WindowListener interface
The signature of 7 methods found in WindowListener interface are given below:
- public abstract void windowActivated(WindowEvent e);
- public abstract void windowClosed(WindowEvent e);
- public abstract void windowClosing(WindowEvent e);
- public abstract void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e);
- public abstract void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e);
- public abstract void windowIconified(WindowEvent e);
- public abstract void windowOpened(WindowEvent e);
Java WindowListener Example
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
- import java.awt.event.WindowListener;
- public class WindowExample extends Frame implements WindowListener{
- WindowExample(){
- addWindowListener(this);
-
- setSize(400,400);
- setLayout(null);
- setVisible(true);
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- new WindowExample();
- }
- public void windowActivated(WindowEvent arg0) {
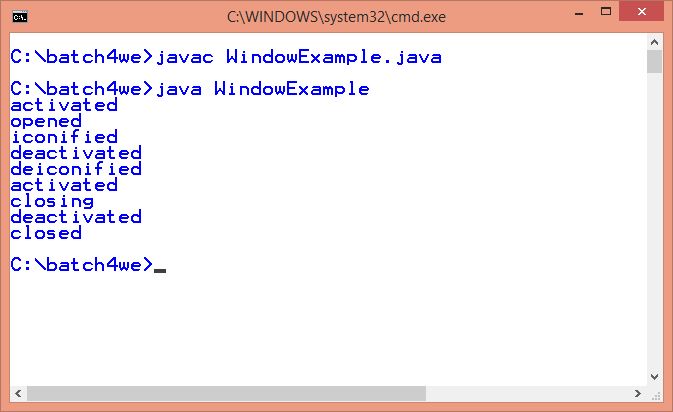
- System.out.println("activated");
- }
- public void windowClosed(WindowEvent arg0) {
- System.out.println("closed");
- }
- public void windowClosing(WindowEvent arg0) {
- System.out.println("closing");
- dispose();
- }
- public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent arg0) {
- System.out.println("deactivated");
- }
- public void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent arg0) {
- System.out.println("deiconified");
- }
- public void windowIconified(WindowEvent arg0) {
- System.out.println("iconified");
- }
- public void windowOpened(WindowEvent arg0) {
- System.out.println("opened");
- }
- }
Output:




Comments
Post a Comment