C++ Exception Handling
Exception Handling in C++ is a process to handle runtime errors. We perform exception handling so the normal flow of the application can be maintained even after runtime errors.
In C++, exception is an event or object which is thrown at runtime. All exceptions are derived from std::exception class. It is a runtime error which can be handled. If we don't handle the exception, it prints exception message and terminates the program.
Advantage
It maintains the normal flow of the application. In such case, rest of the code is executed even after exception.
C++ Exception Classes
In C++ standard exceptions are defined in <exception> class that we can use inside our programs. The arrangement of parent-child class hierarchy is shown below:
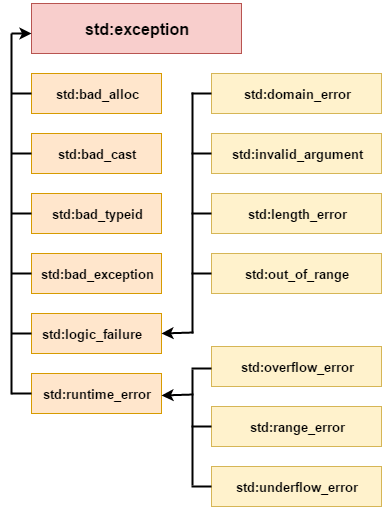
All the exception classes in C++ are derived from std::exception class. Let's see the list of C++ common exception classes.
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| std::exception | It is an exception and parent class of all standard C++ exceptions. |
| std::logic_failure | It is an exception that can be detected by reading a code. |
| std::runtime_error | It is an exception that cannot be detected by reading a code. |
| std::bad_exception | It is used to handle the unexpected exceptions in a c++ program. |
| std::bad_cast | This exception is generally be thrown by dynamic_cast. |
| std::bad_typeid | This exception is generally be thrown by typeid. |
| std::bad_alloc | This exception is generally be thrown by new. |
C++ Exception Handling Keywords
In C++, we use 3 keywords to perform exception handling:
- try
- catch, and
- throw
C++ try/catch
In C++ programming, exception handling is performed using try/catch statement. The C++ try block is used to place the code that may occur exception. The catch block is used to handle the exception.
C++ example without try/catch
Output:
Floating point exception (core dumped) C++ try/catch example
Output:
Attempted to divide by zero!C++ User-Defined Exceptions
The new exception can be defined by overriding and inheriting exception class functionality.
C++ user-defined exception example
Let's see the simple example of user-defined exception in which std::exception class is used to define the exception.
Output:
Enter the two numbers :
10
2
x / y = 5
Output:
Enter the two numbers :
10
0
Attempted to divide by zero!
Comments
Post a Comment